Want to do research? Contact Me!
Design of a Flow Zn | Fe^(3+) Battery with Nafion Membrane for Storage of Solar Energy in Puerto Rico
Abstract
This project proposes the design, construction, and evaluation of an H-Cell redox flow battery using a Nafion membrane and the Zn|Fe^(3+) redox couple as a viable and sustainable alternative for solar energy storage in residential environments. This initiative arises in response to the growing need for decentralized energy solutions, especially in regions such as Puerto Rico, where the electrical system faces frequent failures, unstable infrastructure, and vulnerability to natural disasters.
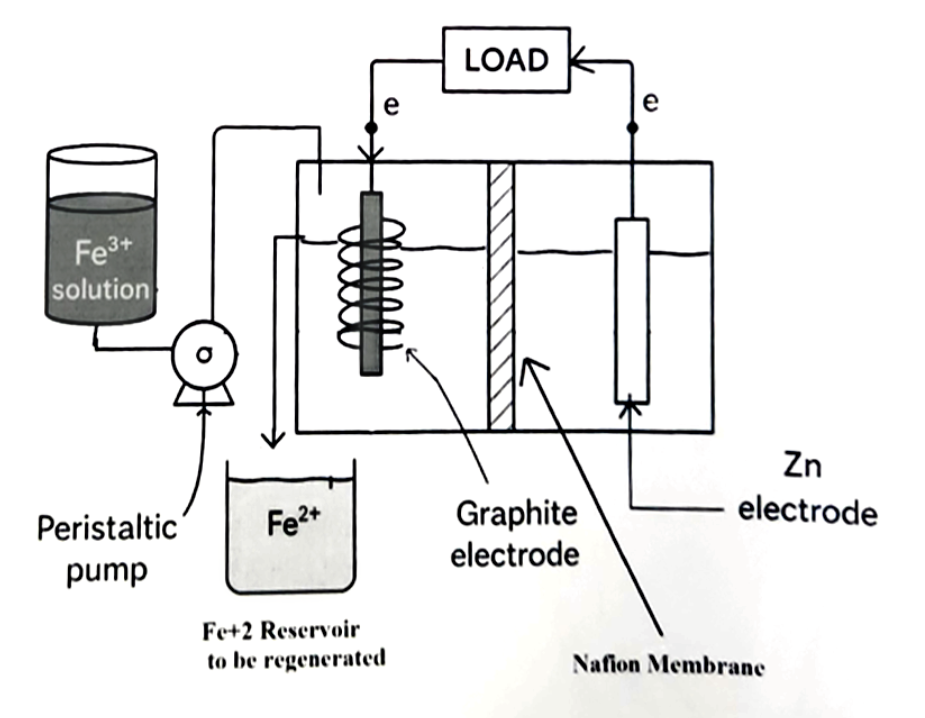


Previous Research
Applied Fluid Dynamics: Flow Through Control Valves using Solidworks Flow Simulation.
Quantitative Analysis of Receptor-Mediated Cell Adhesion to Artificial Surfaces
Abstract
In recent years, the study of cell adhesion to surfaces has been of increasing clinical and research interest. This process is important in events such as cell affinity chromatography, blood clotting and immunological processes. Further, the success of an artificial implant will often depend on the adherence behavior of tissue cells to the implant. However, little fundamental knowledge exists about the kinetics of cell attachment and detachment or the strength of cell-surface adhesion forces and on how these processes depend on the environment. in an attempt to remedy this situation, we pursued a fundamental study on receptor-mediated cell adhesion to surfaces coated with specific binding groups. Liposomes bearing the protein glycophorin were used as cell-like models. Glass microscope slides coated with the protein wheat-germ agglutinin, which possesses a strong affinity for the protein glycophorin, were used as the bottom part of a parallel plate flow chamber (PPFC) apparatus. In order to simulate the shear force which cells might experience in an in vivo situation, a solution was passed over the artificial cells which were attached on the wheat-germ coated surface. The process of shearing glycophorin liposomes from coated-glass surfaces was viewed and recorded through a video-camera/monitor system installed over a Zeiss inverted microscope. This apparatus allowed us to measure the glycophorin liposome detachment kinetics as a function of incubation time, shear flow rate and glycophorin receptor density.
–
–
–
–